In this lab experience we'll introduce a humanoid robot, the Robovie-X, and the use of an XBOX 360 Kinect sensor to record some human movements that will be remapped into and reproduced by the robot. On one hand, we'll use a Kinect sensor for the data acquisition, on the other hand we'll use rviz and Gazebo tools to reproduce the human recorded poses through the robot.
In the following, the procedure for having a working tool is described:
Step 1: Setup and test Kinect and skeleton tracker
First of all, we have to create our workspace:
cd projects mkdir ActionModel cd ActionModel svn co --username ros \ https://robotics.dei.unipd.it/svn/iaslab/projects/ActionModel/src .
Now lets make sure that ROS can find your new package. It is often useful to call rospack profile after making changes to your path so that new directories will be found:
rospack profile && rosstack profile roscd ActionModel cmake -G"Eclipse CDT4 - Unix Makefiles" rosmake
Run the ActionModel plugin from a "launch" file:
roslaunch ActionModel openni_tracker.launch
If all run correctly, you should get something like this:
... frame id = openni_rgb_optical_frame rate = 30 file = /opt/ros/electric/stacks/unipd-ros-pkg/ActionModel/config/tracker.xml InitFromXml... ok Find depth generator... ok Find user generator... ok StartGenerating... ok ...
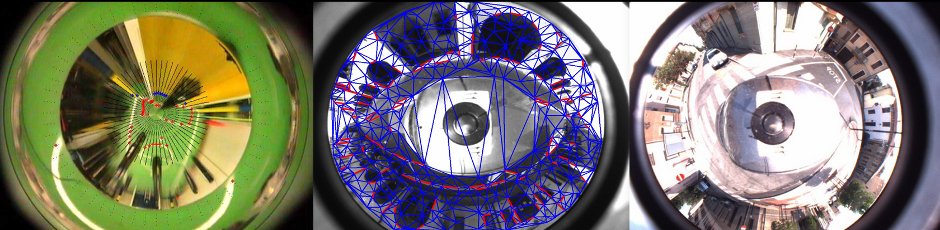
Now, if a person goes in front of the camera, a new user is identify. In order to calibrate the system and track the user with respect to the Kinect, the person have to assume a "Psi Pose" like in Figure 1.
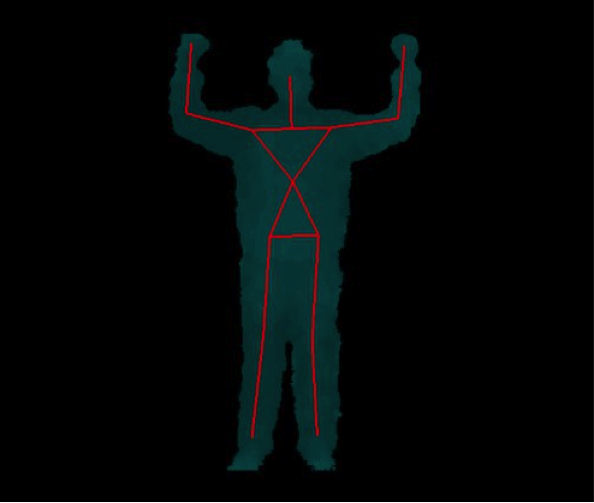

If all run correctly you see:
... New User 1 Pose Psi detected for user 1 Calibration started for user 1 Calibration complete, start tracking user 1
Visualize the tracked person by starting the :
rosrun rviz rviz
and setup some basic properties:
- Fixed frame: /openni_camera
- Add: pointCloud2
- Topic: /camera/rgb/points
- ColorTransform: RGB8
- Style: points
- Add: TF
You should see something like this:

This package provides a set of tools for recording from and playing back to ROS topics. You will use it to record tf trasforms.
Task 1: Remapping of the human joints into the correspondent ones of the Robovie-X
tf is a package that lets the user keep track of multiple coordinate frames over time. tf maintains the relationship between coordinate frames in a tree structure buffered in time, and lets the user transform points, vectors, etc. between any two coordinate frames at any desired point in time, and allows you to ask questions like:
- Where was the head frame relative to the world frame, 5 seconds ago?
- What is the pose of the object in my gripper relative to my base?
- What is the current pose of the base frame in the map frame?
You have to write a tf listener (C++) through which get access to frame transformations.
Suggestion:
#include <tf/transform_listener.h>
...
...
...
tf::TransformListener listener;
ros::Rate rate(10.0);
while (node.ok()){
tf::StampedTransform transform;
try{
listener.lookupTransform("/robovieX2", "/robovieX1",
ros::Time(0), transform);
}
catch (tf::TransformException ex){
ROS_ERROR("%s",ex.what());
}
...
}
...
You will use it in conjunction with the joint_state_publisher in the next task in order to exploit these data to control the robot in Gazebo.
Task 2: Test your Robovie-X in Gazebo
Setup your workspace environment by downloading the robovie_x_gazebo_plugin and robovie_x_model plugins.
cd projects svn co --username ros \ https://robotics.dei.unipd.it/svn/iaslab/projects/robots\ /RobovieX/robovie_x_gazebo_plugin svn co --username ros \ https://robotics.dei.unipd.it/svn/iaslab/projects/robots\ /RobovieX/robovie_x_model
Build and launch your packages:
rospack profile && rosstack profile roscd robovie_x_gazebo_plugin cmake -G"Eclipse CDT4 - Unix Makefiles" rosmake roscd robovie_x_model cmake -G"Eclipse CDT4 - Unix Makefiles" rosmake roslaunch robovie_x_gazebo_plugin gazebo_robot.launch
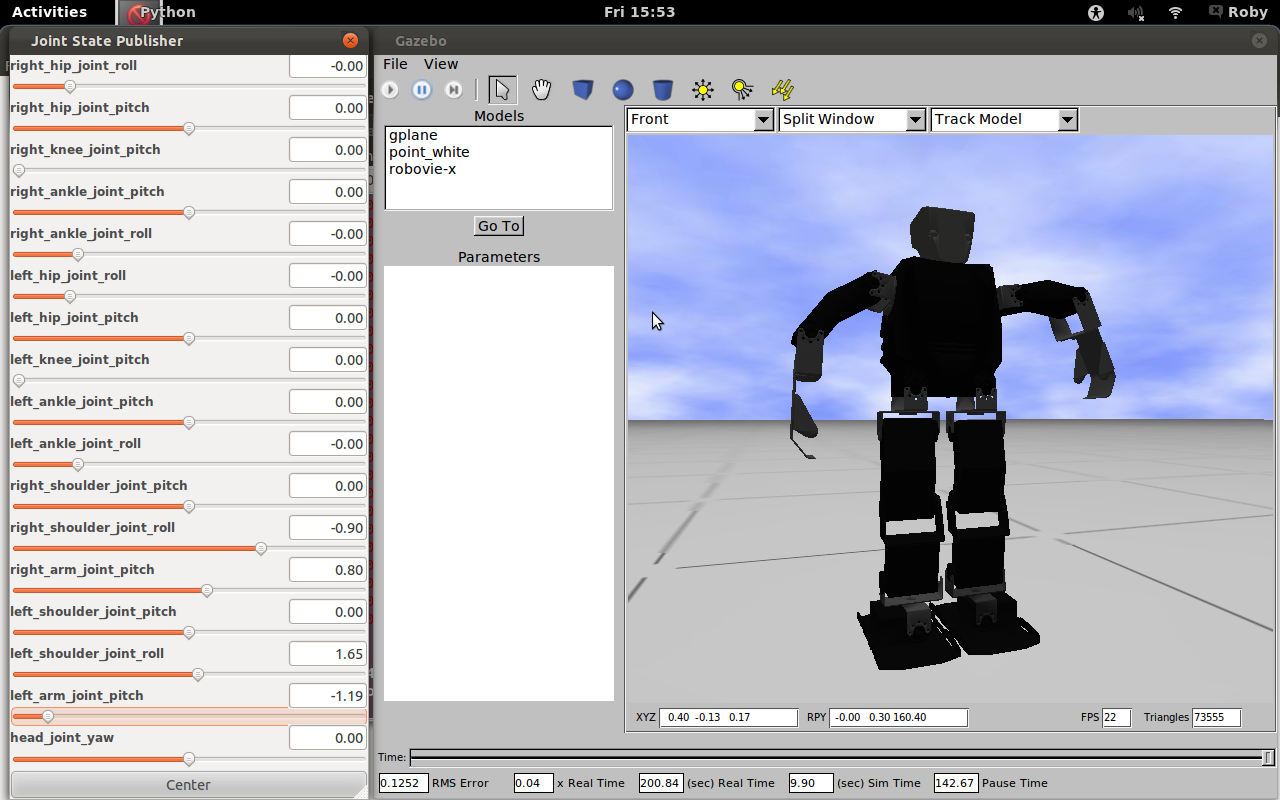
You have to become practical with the GUI, the robot model and to explore the mechanism control underlying the movement.
Task 3: Move the Robovie-X using data acquired through Kinect
You have to control the Robovie-X model into Gazebo by using the joint_state_publisher plugin through the sensor_msgs/JointState:
Header header string[] name float64[] position float64[] velocity float64[] effort
A node for publishing joint angles, either through a GUI, or with default values. This package publishes sensor_msgs/JointState messages for a robot. The package reads the robot_description parameter, finds all of the non-fixed joints and publishes a JointState message with all those joints defined.
The joint angles published from joint_state_publisher will be listened from tf listener and sent to the robot controller to move each non-fixed joint.
Suggestion: start from the upper body part.
That's all, have fun!!!